Back Pain - Causes, Symptoms
Center : Spine Center

It is the most common pain in everyday life after neck pain. Which is common in working age and the elderly. In most cases, 80-90% of patients recover on their own in 4-8 weeks, so the correct treatment may reduce back pain.
Table of Contents
Causes of Back Pain
- Impaired posture or posture, such as sitting and working in a bent back or bent down for long periods, lifting heavy objects from the floor without bending your knees, etc.
- Bone and muscle diseases which is the most common cause, such as a herniated discs, Degenerative spine, Spinal tumor or diseases in the group of connective tissues that are caused after inflammation until the patient has a stiff back, etc.
- Mental conditions, such as stress, can cause the back muscles to contract all the time and cause pain
- Other causes include diseases of the internal organs that can cause back pain such as nephrotic syndrome, ovarian and uterine disease. Abdominal aneurysm disease or cancer that has metastasized to the spine, etc.
Back Pain Symptoms
Pain in the lower back or there may be pain in the hips or legs. Pain may come and go, or persistent pain is associated with pathways, such as increased pain when standing, walking, and in some cases, numbness, leg weakness, or unusual stool and urination problems.
When to see a doctor
- Sudden, unusually intense pain.
- Chronic low back pain that has not been cured for more than 3 months or has become unbearable to the extent that it interferes with daily activities (standing up, sitting, standing, walking).
- Back pain radiating down the leg, with symptoms that come and go for 2 weeks in a row.
- Severe pain at night.
- Can't bend the ankle, leg pain, leg numbness and leg weakness clearly, leg is atrophy.
- Loss of appetite and rapid weight loss.
- Uncontrollable excretion or urinary incontinence.
These symptoms can be diagnosed primarily through a history and physical examination. Additional tests may be done to confirm the diagnosis with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which can quickly diagnose back pain at the source. Able to tell the extent of the disease, allowing the doctor to plan further treatment.
How to treat Back Pain
This is because the most common causes of back pain are diseases of the spine and muscles. Therefore, the important prevention and treatment of back pain are:
- Resting, in patients with severe back pain, for example pain from a herniated disc in the acute phase. Should lie down on a mattress that is tight and less collapsed. Made of pressed cotton or made with coconut fiber
- Correct Positioning, such as sitting, standing, or lifting heavy objects.
- Controlling or losing weight for people who are overweight, this is because back pain hurts much more than people with proper weight.
- Drug treatment Pain relievers such as paracetamol or aspirin may be taken every 4-6 hours, if taking the medication for 5-7 days but the symptoms does not improve, consult a doctor.
- Physical therapy for patients with extreme pain or chronic pain. Using physical therapy equipment reduces the pain
- Orthotics, such as back support Should be advised by a doctor or physical therapist. Not necessarily all cases
- Muscle loosening with a needle or anesthesia
- Surgery
Back Pain Medical Treatment
Nakornthon’s Spine Center prioritizes palliative treatment over surgical procedure (with an exception in severe cases according to a professional’s judgement). We offer 3 treatment disciplines as below;
- Palliative treatment: taking medicine, doing physiotherapy together with lifestyle adjustment. If the symptoms don’t improve within 3 months, a consideration for other disciplines is needed.
- Non-surgical treatment for spinal rehabilitation:
- Steroid injection: to alleviate the pain, improve inflammation a swollen nerve root caused by disc herniation.
- Radio Frequency (RF) Therapy focusing on facet joints: decrease pain transmission and relieve the pain.
- Injection into the facet joint or nerve at the facet joint: injecting anesthetic combined with steroid into the facet joint or an assumed-to-be-a-root-cause nerve.
- Surgical treatment
- Endoscopy Spine Surgery (ESS): the ultra-minimally invasive spine surgery is done by inserting an endoscope through the skin. The incision is minimal and barely visible. The incision pain after the surgery is little. A risk of infection is low. This procedure also helps save the good tissue surrounding the incision site. The operation ensures fast recovery and discharged from the hospital within 24 hours.
- Lumbar discectomy and fusion: the purpose is to remove all the discs and insert artificial ones instead. Also putting screws between joints to fuse vertebrae together.
- Vertebroplasty with O-arm Navigation: Vertebroplasty is done by injecting cement via minimally invasive incision with the size of a coffee straw. It helps stabilize fractured vertebrae without screws.
Back Pain Self-Treatment
Normally, back pain has no severe causes and can disappear after a while. Those who have back pain can self-treat by following the steps below:
- Taking a painkiller or NSAIDs: ibuprofen.
- Cold compression using ice can help decrease inflammation and improve swelling and reducing bleeding.
- Hot compression helps improve muscle soreness because heat causes vasodilation, resulting in improved blood circulation and pain relief.
- Lie down with back flat on the bed and stretch back muscles: with back flat on the bed (or the floor), arms resting beside the body and then contract the belly for about 10 seconds. Repeat it for 2-3 times.
- Massage: Self-massage will help relieve back and leg pain, rubbing or kneading to improve blood circulation, glands and organs’ function.
Preventing Back Pain
Observe your own gestures and perform them correctly. To prevent stress on the back muscles and bones
1. Sleeping position |
|
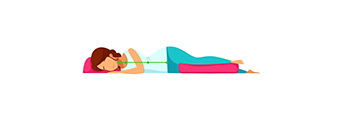 |
The lying position is the best. It is recommended to lie on the lower leg straight out. Upper legs bent at hips and knees. Put a bolster between the legs. |
 |
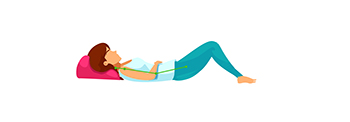
The supine position is a position that may cause the back to bend. Correct this by using a pillow under the knee, so that there is a flexion of the hip and knee joints, this can reduce the deflection of the back |
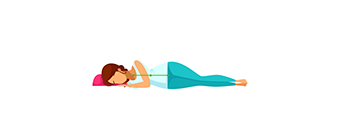 |
The inverted position is the position that causes the spine to bend most. Avoid sleeping in this position. |
2. Sitting position |
|
 |
Chair sitting posture the soles of the feet are placed flat on the background, leaning against the back, hips and thighs in place. On all seats the backrest should not be over 100 degrees and should have armrests to support both arms. |
 |
Car seat- Slide the seat towards the steering wheel. Until your knee is higher than your hip when the brake or gas pedal is pressed or at least to be at the same level When the handle is on the steering wheel Keep your elbows bent for approximately 30 degrees. |
3. Getting up from a chair |
|
 |
To move yourself out, take the edge of the seat Using his hands to stand up, use the strength of your arms and legs to stand up. With your back straight throughout the movement |
4. Standing posture |
|
 |
Put your feet on one leg to stand longer. And to switch legs to rest |
5. Bending / lifting objects from the floor |
|
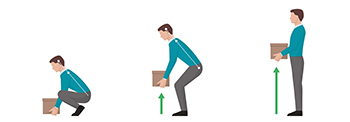 |
Use the method to lower your knees, lift things close to your body, and lift up. Then get up with the strength of the legs, try to keep things close to your body during lifting. |
Exercising the muscles in the back to build flexibility |
|
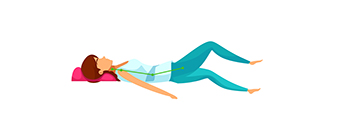 |
Stretching the back-thigh muscles, lie in a supine position, put one knee above the other. Pull your knees in towards your chest, count 1-10, rest. |
 |
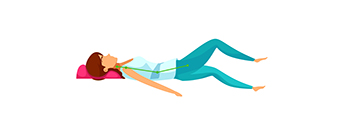
Stretching the posterior thigh muscles, Put your hand under the knee, Pull in until you feel tight, count 1-10 and rest * in case of a degenerative neck problem The head should not be raised. |
Stretching the hips |
|
 |
Lie on your back, bend your knees, cross your right leg to the left until your right foot touches the ground. Then use the left hand to pull the right leg until the torso and right hip feel tight, count 1-10, switch left-right. Try to keep your upper torso as stable as possible. |
Stretching the calf muscles |
|
 |
Stand and lean your hands against the wall. Put one foot behind, knees should be straight and the soles of the feet must stay on the ground. Lower the front of the knee until the leg is stretched, count 1-10, rest. Caution in patients with osteoarthritis. Be careful to bend your knees no more than 90 degrees. |
Exercising your back muscles to build strength |
|
 |
Abdominal muscle type 1 Lie on your back with 2 knees bent, hands crossed, head and shoulder blades up slightly off the floor. Feel that the abdominal muscles are tense counting 1-5 and rest. |
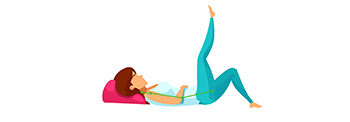 |
Abdominal muscle type 2, lie on your back, 2 knees bent, one leg slightly extended. While contracting the abdominal muscles, count 1-10 and rest |
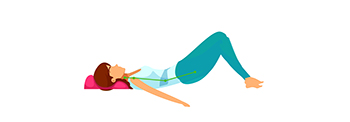 |
Hip muscles lie supine, knees contracted, abdominal muscles. Along with contracting the prolapse muscles By making a bow to the bottom to float off the floor, count 1-10 and rest |

Conclusion
Back pain is caused by muscle soreness and inflammatory pain in tendon and tissues, most commonly found in office workers who work in a prolonged position. Repetitive muscle usage may lead to Office Syndrome, but the good news is, the symptoms can improve by itself within 2-3 days after taking medication or stop doing activity that aggravates the pain.
However, in case back pain has been chronic for more than 3 months or has been on-and-off more than 2 weeks, or radiates to the leg including numbness, weakness, or together with urinary and fecal incontinence, it may indicate spine disorders: disc herniation, spondylosis, and spondylolisthesis.
As a result, it is recommended that those who have these symptoms to receive an additional examination by MRI, as the cause can be varied. A physician’s experience is important to correctly diagnose, so the patient will know how to prevent and treat promptly.
For more information, please contact:
- - Website : https://en.nakornthon.com
- - Facebook : Nakornthon Hospital - International Patient
- - Line : @nakornthoninter
- - Tel: 02-450-9999 (Available 24 hours)
Online Consultation
Article of Spine Center